Aviation is one of the biggest beneficiaries of GIS. Geographic systems are used in various tasks in the airport as well as management of aircraft. The kinds of GIS used in aviation must be very accurate, efficient, and reliable. It must also work on a real-time base to ensure a smooth running of the airports and flights at large. GIS ability to offer distributed and multi-tasking processing enables various activities to be coordinated all at the same time. This is not achievable through manual methods.
List of Application of GIS in Aviation.
1. Aviation structures management: Many tall structures like towers and buildings are monitored using GIS. Surveying on these structures is very important. GIS can be integrated even to manage control of automated tasks in some of these structures found at the airport. Communication between different towers or buildings at the airport is also manageable through GIS.
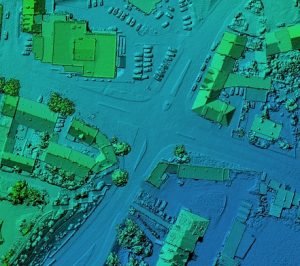
2. Airport layout planning: 3D visualization is among the pros of having GIS. GIS is, in most cases applied during the design period. Three-dimensional layouts of land and structures are presented between teams of engineers and experts to realize a secure and efficient system of transport. The designs can be tested for errors, a simulation is done as well as ideas discussed on how the designs can be improved. The 3D ability of geographic information systems also ensures specific properties to be captured; hence, finer designs and model are achieved. GIS application does not only end during the construction of the airport but is also continued during the running of daily activities at the airport.
3. Flightpath monitoring: Most airports and airstrips have radars that make use of radio waves to communicate. These radars are usually integrated with geographic information systems to offer real-time tracking of aircraft. An aircraft traveling over the sea or even land is identifiable by the nearest radar. GIS has for long been used in aviation to provide path monitoring for the aircrew and airport management. Routes can be mapped digitally and availed to the pilots while at any place on earth. Incase emergencies the same system is used to identify last known locations for emergency response. Investigations on the cause of flight tragedies can be done through flight monitoring to understand what might have caused failures by the aircraft with relation to the routes undertaken.
4. Risk and security evaluation: Security authorities at the airport can conduct crime mapping and prediction for quick and informed decisions making as the kind of GIS used student are very accurate on probabilistic issues. During terror attacks that may happen any time, GIS integrated satellite imaging services may be used to provide visualization on the airport.
5. Airport lighting control: Airport lighting is very crucial. It ensures that operations at the airport are done with ease and normally. Most runways are also marked with lighting facilities to guide pilots as they land and take-off during the night. These lights are best controlled by use of Geographic information systems that offer real-time control mechanisms. The system automatically lights the airport when it’s dark by sensing the absence of sunlight as well as performs shutting down of lighting utilities during the day. This saves humans the significant work that would be involved in lighting the airport manually. It also proves to be quicker and efficient.
6. Environmental and weather assessment: storms are a great hindrance to flight operations. GIS can be integrated with weather systems to ensure that conditions that flights are canceled for safety reasons when necessary. Also, in places that experience lots of volcanic activities that can prevent aircraft from flying, GIS is solely responsible for gathering crucial datasets that can be sampled to produce reports. These reports can then be used to plan whether airplanes fly or not and if yes, the routes to be taken are also identified. Lots of research work done about the effects and impacts that are brought about by the airport being in a given location are also analyzed and stored by GIS. GIS is thus of great help in weather and environmental assessment.
7. Capacity planning: Everything starting from cargo areas, aircraft parking bays, passenger terminus, and many other areas should be well crafted to hold even bigger capacities of traffic, vehicles, aircraft, and people. Strategic planning on space and mapping of airports are some of the critical roles achieved by GIS in aviation.
8. Parking management: Most people who are willing to travel bring along their cars. The airport must, therefore, have a well-integrated system to monitor parking areas all around. GIS may be well designed to serve as a platform where users can query and lookup for map addresses on empty parking slots. This can fasten activities at the airport for visitors who wish to park their vehicles.



Tasie sophie
23 Sep 2021I am a surveying and geoinformatics student
hope I can get a job in the field of aviation
Korede Ewenla
12 Nov 2021yes you can, Most National aviation services providers have a GIS/surveying and Geoinformatics department for aeronautical information services(AIS), NAVAIDs (navigational aids department ),aeronautical Chart services (ACS) . in some countries these are departments on their own . In others, A unified surveying Unit manages all Surveying/GIS related works in the airport environment.
Peter
22 Jun 2022Am Geomatician, can I get a job in Aviation industry?