Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system build to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage and display all kinds of spatial or geographical data. GIS application are tools that allow end users to perform spatial query, analysis, edit spatial data and create hard copy maps. In simple way GIS can be define as an image that is referenced to the earth or has x and y coordinate and it’s attribute values are stored in the table. These x and y coordinates are based on different projection system and there are various types of projection system. Most of the time GIS is used to create maps and to print. To perform the basic task in GIS, layers are combined, edited and designed.
GIS can be used to solve the location based question such as “What is located here” or Where to find particular features? GIS User can retrieve the value from the map, such as how much is the forest area on the land use map. This is done using the query builder tool. Next important features of the GIS is the capability to combine different layers to show new information. For example, you can combine elevation data, river data, land use data and many more to show information about the landscape of the area. From map you can tell where is high lands or where is the best place to build house, which has the river view . GIS helps to find new information.
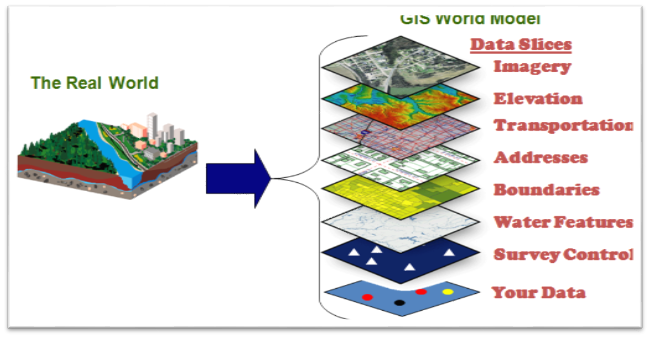
Gis Model
How GIS Works:
-
Visualizing Data: The geographic data that is stored in the databases are displayed in the GIS software.
-
Combining Data: Layers are combined to form a maps of desire.
-
The Query: To search the value in the layer or making a geographic queries.
Definition by others:
A geographic information system (GIS) lets us visualize, question, analyze, and interpret data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends. (ESRI)
In the strictest sense, a GIS is a computer system capable of assembling, storing, manipulating, and displaying geographically referenced information (that is data identified according to their locations). (USGS)
Advantage of GIS:
-
Better decision made by government people
-
Improve decision making with the help of layered information
-
Citizen engagement due to better system
-
Help to identify communities that is under risk or lacking infrastructure
-
Helps in identifying criminology matters
-
Better management of natural resources
-
Better communication during emergency situation
-
Cost savings due to better decision
-
Finding different kinds of trends within the community
-
Planning the demographic changes
History of GIS:
Modern GIS has seen series of development. GIS has evolved with the computer system. Here are the brief events that has happened for the development of the GIS system.
Year 1854 – The term GIS that used scientific method to create maps was used by John Snow in 1854. He used points on London residential map to plot outbreak of Cholera.
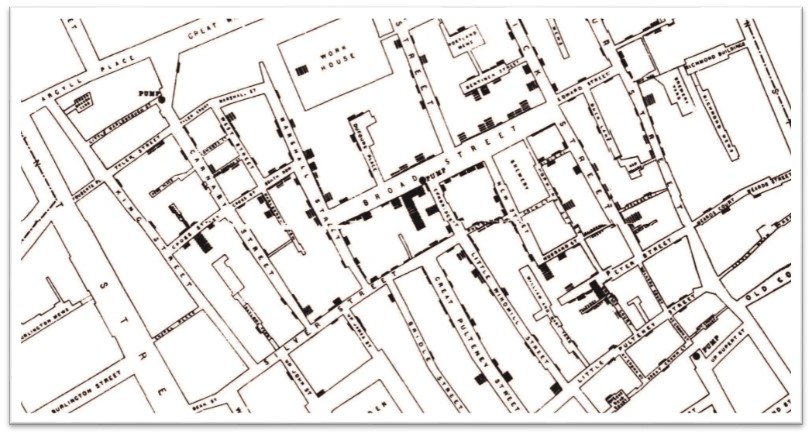
John Snow Cholera Outbreak Map
Year 1960 – Modern computerized GIS system began in year 1960.
Year 1962 – Dr. Roger Tomlinson created and developed Canadian Geographic Information System (CGIS) to store, analyze and manipulate data that was collected for the Canada Land Inventory (CLI). This software had the capacity to overlay, measurement and digitizing (converting scan hardcopy map to digital data). It is never provided in commercial format but Dr. Tomlinson is the father of GIS.

Dr. Roger Tomlinson (1933-2014)
Year 1980 – This period saw rise of commercial GIS software’s like M&S Computing, Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) and Computer Aided Resource Information System (CARIS). These all software were similar to CGIS with more functionality and user-friendliness. Among all the above the most popular today is ESRI products like ArcGIS, ArcView which hold almost 80 % of global market.
Component of GIS:
Hardware: Hardware is the physical component of the computer and GIS runs on it. Hardware may be hard disk, processor, motherboard and so on. All these hardware work together to function as a computer. GIS software run on these hardware. Computer can be standalone called desktop or server based. GIS can run on both of them.
Software: GIS Software provides tools and functions to input and store spatial data or geographic data. It provides tool to perform geographic query, run analysis model and display geographic data in the map form. GIS software uses Relation Database Management System (RDBMS) to store the geographic data. Software talks with the database to perform geographic query.
Data: Data are the fuel for the GIS and the most important and expensive component. Geographic data are the combination of physical features and it’s information which is stored in the tables. These tables are maintained by the RDBMS. The process of capturing the geographic data are called digitization which is the most tedious job. It is the process of converting scanned hardcopy maps into the digital format. Digitization is done by tracing the lines along the geographic features for example to capture a building you will trace around the building on the image.
People: People are the user of the GIS system.
People use all above three component to run a GIS system. Today’s computer are fast and user friendly which makes it easy to perform geographic queries, analysis and displaying maps. Today everybody uses GIS to perform their daily job.
Types of GIS Data:
Raster Data: Raster data store information of features in cell based manner. Satellite images, photogrammetry and scanned maps are all raster based data. Raster model are used to store data which varies continuously as in aerial photography, a satellite image or elevation values (DEM- Digital Elevation Model).
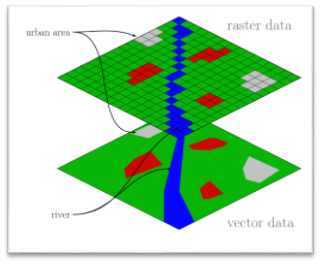
Vector Data: There are three types of vector data, points, lines and polygons. These data are created by digitizing the base data. They store information in x, y coordinates. Vectors models are used to store data which have discrete boundaries like country borders, land parcels and roads.
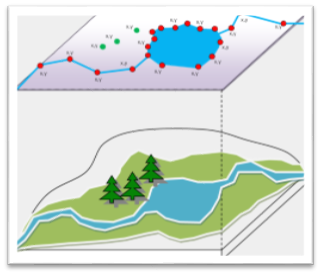
Advantage and Disadvantage of using raster and vector Data
-
Raster data model record value of all the points of the area covered which required more data storage than model represented by the vector model.
-
Raster data is less expensive to create computationally compare to vector graphics.
-
Raster data has issue while overlaying multiple images.
-
Vector data are easily overlaid, for example overlaying roads, rivers, land use are easier than raster data.
-
Vector data are easier to scale, re-project or register.
-
Vector data are more compatible with the relational database management system.
-
Vector file sizes are way smaller than raster image file sizes.
-
Vector data are easier to update like adding river stream but has to be recreated for the raster image.
Raster Formats
-
ADRG – ARC Digitized Raster Graphics
-
RPF – Raster Product Format, military
-
DRG – Digital raster graphic
-
ECRG – Enhanced Compressed ARC Raster Graphics
-
ECW – Enhanced Compressed Wavelet (from ERDAS
-
Esri grid –ASCII raster formats used by ESRI
-
GeoTIFF – TIFF variant enriched with GIS relevant metadata
-
IMG – image file format used by ERDAS
-
JPEG2000 – Open-source raster format
-
MrSID – Multi-Resolution Seamless Image Database
Vector Formats
-
AutoCAD DXF –AutoCAD DXF format by Autodesk
-
Cartesian coordinate system (XYZ) – simple point cloud
-
DLG – Digital Line Graph (USGS format)
-
GML – Geography Markup Language – Open GIS format used for exchanging GIS data
-
GeoJSON – a lightweight format based on JSON, used by many open source GIS packages
-
GeoMedia – Intergraph’s Microsoft Access based format for spatial vector storage
-
ISFC – Intergraph’s MicroStation based CAD solution
-
Keyhole Markup Language KML – Keyhole Markup Language a XML based
-
MapInfo TAB format – MapInfo’s vector data format
-
NTF – National Transfer Format
-
Spatialite – is a spatial extension to SQLite,
-
Shapefile – Most popular vector data developed by Esri
-
Simple Features – specification for vector data
-
SOSI – a spatial data format used for all public exchange of spatial data in Norway
-
Spatial Data File – Autodesk’s high-performance geodatabase format
-
TIGER – Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing
-
(VPF) – Vector Product Format
Tech Tip: Experience the ease of comfort to load/access your essential GIS applications at your convenience with remote accessibility on any device(PC/android/iOS) with virtual PCs from www.CloudDesktopOnline.com with 24*7 top-notch technical support from one of the best DaaS providers – Apps4Rent.

dauda balami
26 May 2015Gis at a finger tip,so interesting.
admin
26 May 2015Thank you Dauda, appreciate for your comment
suman
11 Jul 2015Good Initiative. Carry on plz
admin
12 Jul 2015Thank you Suman, appreciate for your comment
Yakubu Magaji
13 May 2016very educative lesson,develop more!
admin
26 May 2016Thank you Yakubu, appreciate for your comment
Fabricio Ortiz
11 Oct 2016Thanks for the article. It was very usefull.
admin
11 Oct 2016Thank You.
William Eric Huggins
5 Nov 2016Hello!,
I am a Student, learning GIS, and I ASK THAT PLEASE email me back, AND SEND ME SOME INFORMATION, ON HOW GIS IS USED IN THE AREA OR FIELD OF Environmental Design? I AM LOOKING FOR A CAREER JOB, THAT USES GIS, AND IF YOU CAN EVEN MAIL ME SOME INFORMATION ABOUT ENVIRONMENTAL Design, The organization called: EDRA.ORG, I WOULD APPRECIATE IT MICH. I LOOK TO YOUR REPLY.
Thank you
William Eric Huggins
P.O. Box 96
Randallstown, Md. 21133
admin
5 Nov 2016I will send u in your mail box.
Amir
13 Mar 2017Hi Admin!
I am very pleased for you helpful and supportive materials concerning GIS and I would kindly ask you to send me via my email address.
I actually appreciate and recognize your valuable learning materials.
Sorry, I would like to know how can geophysical,geological,geochemical and magnetic datasets can be combined in GIS to yield effective decision making process?
Please, assist me.
Best regards,
Amir.
admin
13 Mar 2017Thanks Amir, I will see what I can find out about the discipline you mentioned. Few GIS application I have mentioned on one my post, please have a look http://grindgis.com/blog/gis-applications-uses
Amir
13 Mar 2017Thanks Admin for your strong cooperation!
I am waiting for your assistance and it is my hope that the issues will be definitely resolved.
Thanks very much.
Amir.
Amir
14 Mar 2017Hello !
I am just to remind you on the issues that I had told you yesterday.
Good Day,
Amir.
Abdul Ghaffar
28 Sep 2017Hi….. I am university student… I read about GIS a few days ago… Now I decided to read it properly and want to do some research work on it…. So plz guide me regarding this……
Abdul Ghaffar
Sialkot, Pakistan
admin
4 Oct 2017Let me know what you are looking for?
jemika
29 Oct 2017Really awesome site
Thanks for great information
#rock.n roll****.
admin
1 Nov 2017Thank you Jemika
Kofi Okyere
17 Feb 2018Please what is the use of “like” ,”in” ,”is” ,”null” ,”like” and “not” related to select by attributes in the selection word
admin
18 Feb 2018http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/map/working-with-layers/building-a-query-expression.htm
harsha vardhan
10 Mar 2018Hii……
I get to know this is one of the useful and helpful site by guidance.
If there is a possibility can you help me with this…
I’m interested to get internship on GIS ,so can you please help with this……
harsha,
INDIA.
admin
13 Mar 2018Yes tell me what type of help you are looking for?
Mensah Samuel messagye
26 Mar 2018Tnx for ur website
admin
28 Mar 2018Thank you Mensah
KARTIK
19 May 2018Great Information ????????
Michael ochieng
22 May 2018important topic to study
Michael ochieng
22 May 2018important topic to study,just do more inventions on it.
KHALID JAMAL
4 Jun 2018my name is Khalid Jamal, Iam a student at the institute of rural development planning Tanzania bachelor degree my course is bachelor degree of regional planning. I ask about the application of GIS in settlement planning.
KHALID JAMAL
4 Jun 2018what are the application of GIS in settlement planning
Bruno
29 Aug 2018Good day please am an environmental geology student, I would like to know if GIS could be used to assess groundwater, if its possible, how could that be achieved, i want to do a research on how gis and remote sensing could be used to assess groundwater potential and quality
Naveen Malga
11 Nov 2018Thankyou so much
Fuad Mohamed
4 Dec 2018Hi sir, thanks for you benefit us information about GIS, am student and your lessons can help me to understand whats GIS , so really i like it the easiest way that you have prepared GIS, so can u plz send pdf book at my email address about this GIS you have prepared, now am waiting for your reply
Thank you
William Eric Huggins
admin
8 Dec 2018You will download the html page and use the available at https://html2pdf.com/
onuoha oc
12 Jan 2019really educative
solomon
12 Mar 2019I am a Student MSC, learning GIS, and I ASK THAT PLEASE email me back, AND SEND ME SOME INFORMATION, ON HOW GIS IS USED IN THE AREA OR FIELD OF Environmental Design? I AM LOOKING FOR A CAREER JOB, THAT USES GIS, AND IF YOU CAN EVEN MAIL ME SOME INFORMATION ABOUT ENVIRONMENTAL Deign. I LOOK TO YOUR REPLY or answer
admin
15 Mar 2019GIS has lots of opportunity, I myself works in the field. Imagine everything in this world has location and information available get attached to x and y.
Dennis Tejero Sabando
27 Mar 2019Dear admin
First time I know about GIS when I attended a meeting regarding disaster and risk management organization. We need this tools for evaluation of certain areas. Could you please send me info on how or application tutorial of gis on how it used in environmental mapping.
Thank you very much.
osamayuosef
17 May 2019what is geographic query
Jamiu Funsho
13 Jun 2019Good day, thanks for your detailed explanation on GIS, as an HSE officer I will like to know how I can make use of GIS in Planning, Monitoring and Enforcing issues of Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Company. Please Help.
Dr.K.Pradeep
28 Jun 2019Actually I am taking GIS class for Petroleum Engineering students. and It is basic introduction of GIS. In this comment i will add the syllabus. kindly send back the materials.
UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF GIS 9
Introduction to GIS – Basic spatial concepts – Coordinate Systems – GIS and Information
Systems – Definitions – History of GIS – Components of a GIS – Hardware, Software, Data,
People, Methods – Proprietary and open source Software – Types of data – Spatial, Attribute
data- types of attributes – scales/ levels of measurements.
UNIT II SPATIAL DATA MODELS 9
Database Structures – Relational, Object Oriented – ER diagram – spatial data models – Raster
Data Structures – Raster Data Compression – Vector Data Structures – Raster vs Vector Models-
TIN and GRID data models – OGC standards – Data Quality.
UNIT III DATA INPUT AND TOPOLOGY 9
Scanner – Raster Data Input – Raster Data File Formats – Vector Data Input –Digitiser –
Topology – Adjacency, connectivity and containment – Topological Consistency rules –
Attribute Data linking – ODBC – GPS – Concept GPS based mapping.
UNIT IV DATA ANALYSIS 9
Vector Data Analysis tools – Data Analysis tools – Network Analysis – Digital Education models –
3D data collection and utilisation.
UNIT V APPLICATIONS 9
GIS Applicant – Natural Resource Management – Engineering – Navigation – Vehicle tracking and
fleet management – Marketing and Business applications – Case studies.
abdoabamecha
20 Jul 2019thanks alot lvery hapy with your honorableresponse
koneru lata
23 Aug 2019thanks a lot. this is very informative
Mahmud
23 Aug 2019I need five different definition of gis, years if the defined and names if the defined
Nipunie Rajasekara
26 Aug 2019hi
I’m a specialized student in geography .and im studing GIS and im working with QGIS.This is so important and thanks for this informations.i would like to tell you , can you made some note of ‘how to work in GIS.’
Thank you
R.G.Nipunie Rajasekara
Kandy,
Sri Lanka
V Mohan Reddy
31 Aug 2019Hi This is Mohan Reddy, from India.
I continue my job in Gis industry past 2 years, I want know please, how to get Gis professional certificate?.
this is help foe my future, is there any institutes in India, please let me know.
Thank you,
Best regards,
Mohan Reddy
admin
31 Aug 2019This is the one that I have, https://www.gisci.org/
Mukesh Kumar
24 Nov 2019सभी GIS उपयोगकर्ताओं के लिए फायदेमंद है क्योंकि यह समझाने में पूर्ण रूप से सक्षम है
Mugiraneza jean claude
28 Nov 2019Hi!! I am claude , a student learning applied statistics and i would like to ask you some question related to GIS how GIS can be used in statistics and if if possible you should send me on my email a prepared well note on that question and olso the application of GIS in statistics and related video teaching about GIS
Thanks regard
jean claude Mugiraneza
Sifon
25 Feb 2020I have really learned a lot, i am currently doing my MSc in GIS and this website has provided me with much information i need.
admin
29 Feb 2020Thank you
Sonia
27 Mar 2020Hi,
May I know the relevant example of data issues in GIS?
Thank you.
Calistas Paul
19 May 2020I’m interested to learn more about GIS, it’s very brilliant technology.
Imran
18 Aug 2022What an awesome content!
A very well written guide for absolute beginners.
Fully explained in layman english.
Thanks a lot…
Toba Alli
29 Sep 2023good summary about GIS it worth reading and making reference to . thanks .